Polysaccharide Based Injectables
Polysaccharide based injectables are becoming increasingly popular as a non-surgical solution for addressing skin aging. These injectables, composed of long chains of sugar molecules, offer a range of benefits for improving skin texture, volume, and overall appearance.
Types of Polysaccharides
There are various types of polysaccharides used in these injectables, each with unique properties and applications. Hyaluronic acid, perhaps the most well-known, is a natural component of skin that attracts and retains moisture, plumping up the skin and reducing the appearance of wrinkles.
Other commonly used polysaccharides include dextran, chondroitin sulfate, and polygalacturonic acid. Dextran is known for its viscosity and ability to stimulate collagen production, while chondroitin sulfate helps maintain cartilage health and can contribute to smoother skin texture. Polygalacturonic acid, derived from pectin, offers hydrating properties and can improve skin elasticity.
Mechanism of Action
Polysaccharide-based injectables work by mimicking the body’s natural processes. They attract and hold water molecules, increasing hydration and plumping the skin. This helps to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, giving a more youthful appearance.
Some polysaccharides also stimulate collagen production, a protein essential for skin structure and firmness. By boosting collagen levels, these injectables can help improve skin elasticity and overall texture.
Benefits of Polysaccharide Injections
Polysaccharide-based injectables offer several benefits for improving skin appearance. Firstly, they provide hydration to the skin by attracting and retaining water molecules, resulting in a plumper and smoother complexion. This can effectively reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, contributing to a more youthful look.
Moreover, some polysaccharides stimulate collagen production, which is crucial for maintaining skin elasticity and firmness. By boosting collagen levels, these injectables can help improve skin texture and overall appearance, reducing the signs of aging.
Additionally, polysaccharide-based injectables are generally well-tolerated with minimal side effects compared to other cosmetic procedures. They offer a non-surgical alternative for addressing skin concerns, making them an attractive option for many individuals seeking to improve their skin’s appearance.
Areas of Treatment
Polysaccharide based injectables are used in various areas of treatment. They can be applied to the face to reduce wrinkles and fine lines, enhance lip volume, and create a smoother skin texture.
Beyond facial rejuvenation, these injectables also find applications in treating scars and stretch marks. They help to improve the appearance of these blemishes by plumping up the skin and promoting collagen production.
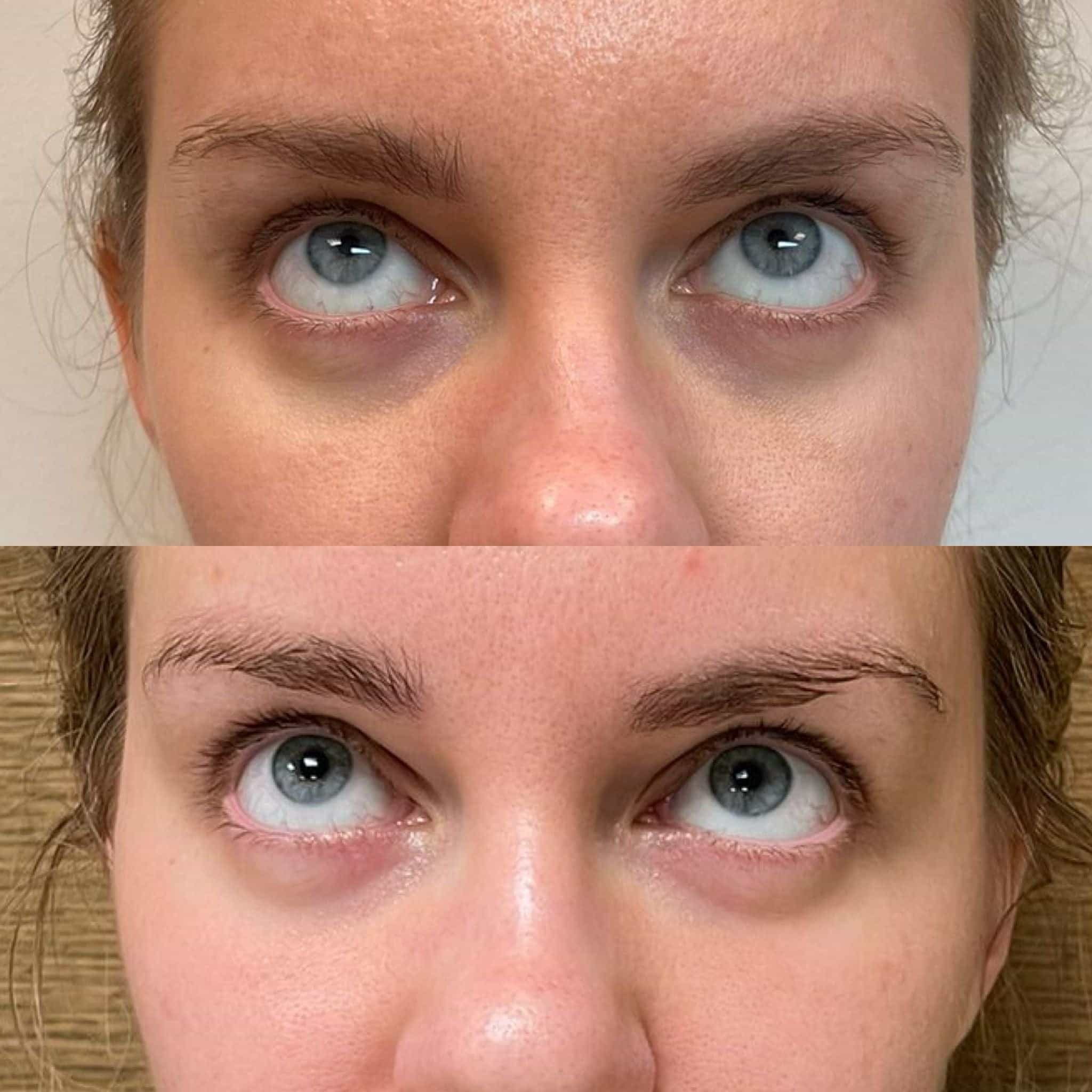
In some cases, polysaccharide based injectables are used for medical purposes, such as wound healing and osteoarthritis treatment. Their ability to attract water and stimulate cell regeneration makes them beneficial in these areas.
Hyaluronic Acid Based Injectables
Polysaccharide-based injectables offer a non-surgical approach to combatting the visible signs of aging. These substances, comprised of chains of sugar molecules, work by mimicking the body’s natural processes to enhance skin hydration, plumping it up and minimizing wrinkles.
Properties and Variations of Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid is a glycosaminoglycan, meaning it’s a complex carbohydrate that forms part of connective tissues in our bodies. It naturally occurs in the skin and plays a crucial role in maintaining hydration by attracting and retaining water molecules. This gives the skin its plumpness and elasticity.
- Hyaluronic acid based injectables work by supplementing the body’s natural hyaluronic acid stores, boosting hydration and improving skin volume.
- They are effective for addressing a range of skin concerns including wrinkles, fine lines, dryness, and loss of volume.
- The varying molecular weights of hyaluronic acid used in injectables determine their specific effects.
Higher molecular weight hyaluronic acids are typically used for deep dermal layers, promoting hydration and volumizing, while lower molecular weight varieties target superficial layers, improving skin texture and reducing fine lines.
Variations in Hyaluronic Acid
- Cross-linked hyaluronic acid: This type is formed by chemically bonding hyaluronic acid molecules together. This creates a stronger gel that lasts longer under the skin, making it suitable for volumizing and contouring treatments.
- Non-cross-linked hyaluronic acid: This type is not chemically modified and dissolves more quickly in the body. It’s often used to address fine lines and wrinkles, providing smoother texture without significant volume change.
Clinical Applications and Results
Hyaluronic acid based injectables are a popular choice for addressing various skin concerns due to their ability to hydrate and volumize.
These injectables work by supplementing the body’s natural hyaluronic acid stores, which naturally attract and retain water molecules, plumping the skin and reducing the appearance of wrinkles.
Hyaluronic acid comes in different molecular weights, tailored for specific applications. Higher molecular weight hyaluronic acids are used for volumizing and contouring, while lower molecular weight varieties target fine lines and improve skin texture.
Cross-linked hyaluronic acid is a more stable form, lasting longer under the skin and ideal for sculpting and enhancing facial features. Non-cross-linked hyaluronic acid, on the other hand, dissolves quicker, making it suitable for smoothing fine lines and wrinkles without significant volume changes.
Clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of hyaluronic acid injectables in reducing wrinkles, improving skin elasticity, and enhancing overall complexion.
Considerations for Hyaluronic Acid Injections
Hyaluronic acid based injectables are a popular choice for addressing various skin concerns due to their ability to hydrate and volumize. These injectables work by supplementing the body’s natural hyaluronic acid stores, which naturally attract and retain water molecules, plumping the skin and reducing the appearance of wrinkles.
Hyaluronic acid comes in different molecular weights, tailored for specific applications. Higher molecular weight hyaluronic acids are used for volumizing and contouring, while lower molecular weight varieties target fine lines and improve skin texture.
Cross-linked hyaluronic acid is a more stable form, lasting longer under the skin and ideal for sculpting and enhancing facial features. Non-cross-linked hyaluronic acid, on the other hand, dissolves quicker, making it suitable for smoothing fine lines and wrinkles without significant volume changes.
Considerations when choosing hyaluronic acid based injectables include the desired outcome, individual skin type and concerns, and consultation with a qualified medical professional. A thorough evaluation of facial anatomy and skin characteristics is essential to determine the appropriate type and amount of hyaluronic acid for optimal results.
Potential side effects of hyaluronic acid injections are generally mild and temporary, including redness, swelling, bruising, and tenderness at the injection site. These typically resolve within a few days.
It’s important to follow post-treatment instructions provided by the medical professional to minimize the risk of complications and ensure optimal healing.
Non-Hyaluronic Acid Polysaccharides
Beyond hyaluronic acid, various other non-hyaluronic acid polysaccharides are utilized in injectables for skin rejuvenation. These include dextran, chondroitin sulfate, and polygalacturonic acid, each offering unique benefits for enhancing skin appearance and health.
Emerging Polysaccharide Options
Dextran is a polysaccharide derived from starch and is known for its ability to stimulate collagen production.
Collagen is a protein essential for maintaining skin structure and firmness. By boosting collagen levels, dextran-based injectables can help improve skin elasticity and reduce the appearance of wrinkles.
Chondroitin sulfate, another polysaccharide found naturally in cartilage, is known to contribute to smoother skin texture.
It is believed to aid in moisture retention and may stimulate the production of hyaluronic acid within the skin, further enhancing hydration and plumpness. Polygalacturonic acid, derived from pectin, offers hydrating properties and can improve skin elasticity.
Potential Advantages and Limitations
Non-Hyaluronic Acid polysaccharides offer potential advantages in skin rejuvenation by targeting specific concerns beyond hydration. Dextran, known for its viscosity and collagen-stimulating properties, can contribute to firmer skin and a reduction in wrinkles. Chondroitin sulfate, found naturally in cartilage, may improve skin texture by promoting moisture retention and potentially boosting hyaluronic acid production.
Polygalacturonic acid, derived from pectin, provides hydrating benefits and can enhance skin elasticity. These polysaccharides offer alternative options for individuals seeking non-hyaluronic acid based solutions for addressing specific skin concerns.
However, it’s important to note that research on the long-term effects and efficacy of some non-hyaluronic acid polysaccharides in injectables is still limited compared to hyaluronic acid. Further studies are needed to fully understand their potential benefits and limitations.
Future Directions in Research and Development
The future of non-hyaluronic acid polysaccharides in injectables for skin rejuvenation holds promising possibilities. Ongoing research aims to explore the full potential of these diverse polysaccharides, particularly dextran, chondroitin sulfate, and polygalacturonic acid.
Investigating their long-term effects and efficacy will provide a clearer understanding of their suitability for various skin concerns.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring innovative ways to combine different polysaccharides in formulations to create synergistic effects, enhancing hydration, collagen production, and skin elasticity.
Development of novel delivery systems that target specific dermal layers could also improve the efficacy and longevity of these treatments.
The search for new, biocompatible polysaccharides with unique properties is ongoing. Discovering novel substances derived from natural sources or through synthetic modifications could lead to groundbreaking advancements in non-surgical skin rejuvenation.
Advancements in nanotechnology may allow for the creation of nanoparticles loaded with polysaccharides, improving their penetration into deeper skin layers and enhancing their effectiveness.
Personalized medicine approaches tailored to individual skin characteristics and concerns could also become more prevalent, utilizing a combination of polysaccharides to achieve optimal results.
Safety and Considerations
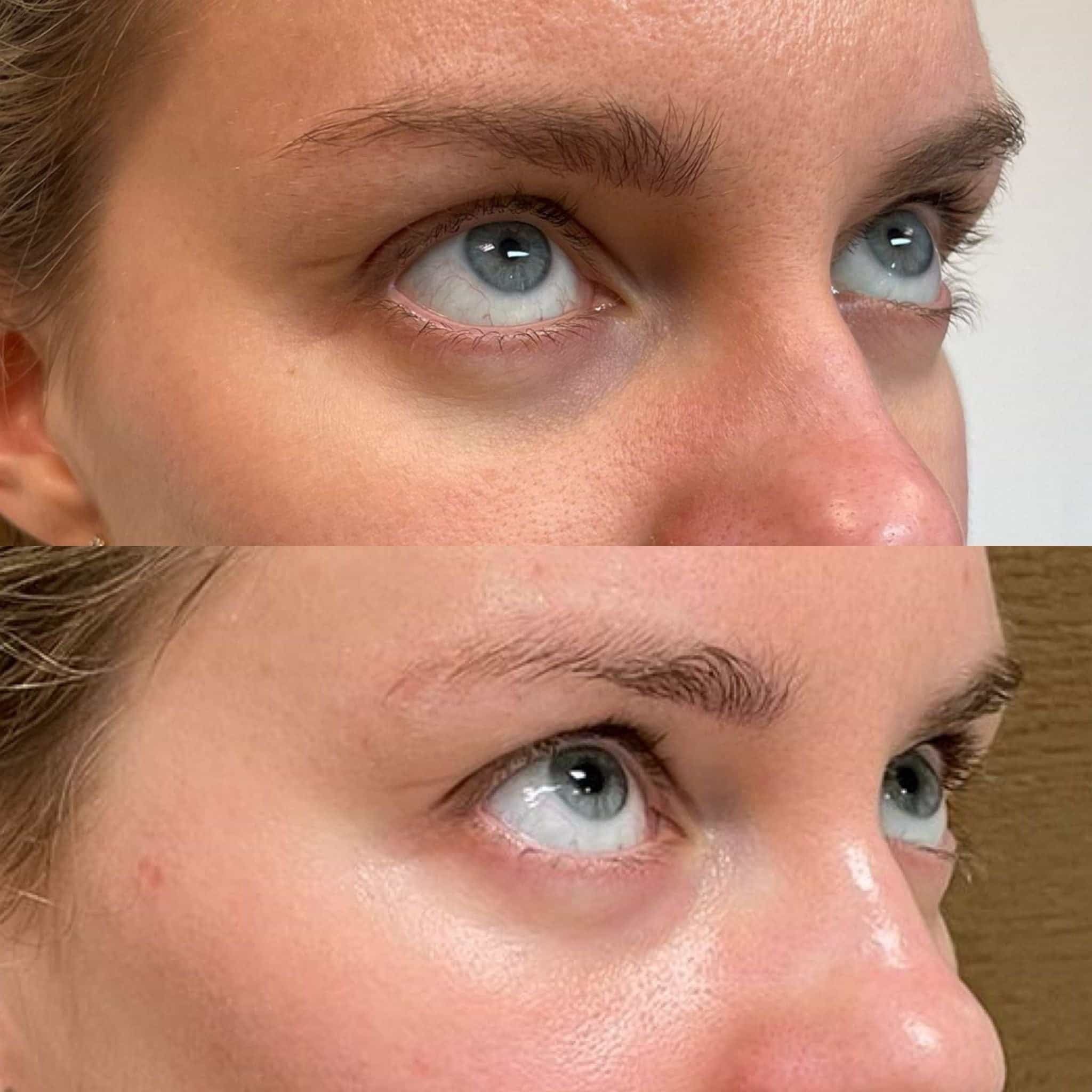
Before considering any treatment involving injectables, it is crucial to prioritize safety and well-being. Consulting with a qualified medical professional who specializes in aesthetic medicine or dermatology is essential. They can assess your individual needs, skin type, and medical history to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Allergic Reactions and Precautions
Safety and Considerations
When considering polysaccharide-based injectables for skin rejuvenation, safety should be paramount. Always seek treatment from a qualified and experienced medical professional who specializes in aesthetic medicine or dermatology. They will assess your individual needs, skin type, and medical history to determine the most suitable treatment plan and minimize potential risks.
Allergic Reactions and Precautions
Although polysaccharide-based injectables are generally well-tolerated, allergic reactions can occur. It’s crucial to inform your medical professional about any known allergies or sensitivities you may have, particularly to substances like hyaluronic acid, dextran, or other ingredients used in the injectables. A thorough review of your medical history will help identify any potential contraindications.
Prior to the procedure, a patch test might be recommended to assess for any allergic reactions to the specific polysaccharide being used.
It’s also essential to follow post-treatment instructions carefully to minimize the risk of complications and ensure optimal healing.
Avoid strenuous activities or exposure to extreme temperatures immediately after treatment.
Be aware that individual responses to injectables can vary, and some people may experience more pronounced side effects than others.
Open communication with your medical professional about any concerns or changes in your condition is crucial throughout the process.
Choosing a Qualified Practitioner
Choosing a qualified practitioner is paramount when considering polysaccharide-based injectables. Look for a medical professional who specializes in aesthetic medicine or dermatology and has extensive experience administering these treatments.
Inquire about their training, qualifications, and certifications to ensure they possess the necessary expertise. A reputable practitioner will thoroughly evaluate your skin condition, discuss potential risks and benefits, and tailor the treatment plan to your individual needs and goals.
Don’t hesitate to ask questions and seek a second opinion if you have any concerns. Your safety and well-being should always be the top priority.
Long-Term Effects and Maintenance
Polysaccharide-based injectables offer several benefits for improving skin appearance, but it’s essential to consider safety and long-term effects.
Safety Considerations: Always choose a qualified medical professional with experience in aesthetic medicine or dermatology. They will assess your individual needs, medical history, and potential allergies before administering any treatment.
Potential Side Effects: While generally well-tolerated, polysaccharide injectables can cause mild side effects like redness, swelling, bruising, and tenderness at the injection site. These usually subside within a few days.
Long-Term Effects: More research is needed on the long-term effects of some polysaccharides, particularly non-hyaluronic acid types. Regular follow-up appointments with your medical professional are essential to monitor your skin’s response and address any concerns.
Maintenance: The duration of results varies depending on the type of polysaccharide used and individual factors. Hyaluronic acid injectables typically last 6-18 months, while other polysaccharides may have longer or shorter durations.
Repeat treatments may be necessary to maintain the desired results. Your medical professional can advise on the appropriate treatment schedule based on your individual needs.
- Dermal Fillers Near Surbiton, Surrey - June 29, 2025
- Dermal Fillers Near Dunsfold, Surrey - June 26, 2025
- Zoophilia Fetish: Understanding And Navigating A Taboo Desire - June 24, 2025
